由于需要一个FTP服务器使用,平时上传下载文档一类的小文件,就买了华为云的服务器,Linux系统,Centos7.4版本,带宽1M比较小,但是个人使用是还可以的。但是搭建FTP服务器的过程是很狗血的,网络上的资料零散而千头万绪,一顿采坑,终于在本人的坚持努力下,经历了几次三番的VM虚拟机上的vsftpd服务的安装卸载后,搞定了。出于我不为大家填坑,谁为大家填坑的精神,将搭建的最终版配置共享给大家,将遇到的问题解决方法分享给大家,希望可以帮助需要的你。本文只对vsftpd服务器的搭建进行初步配置操作,距离多用户、大数据量访问使用ftp服务器还有一定差距,具体配置项可以自行查询资料进行配置。使用Linux系统用户登录ftp,不涉及虚拟用户登录。
Linux的命令以红色标注,vsftpd.conf的配置文件中关键的位置做了注释,复制的时候,需要把注释删除。
一、vsftpd安装
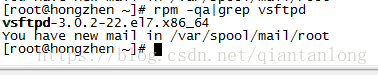
1、rpm -qa|grep vsftpd 检查是否安装
如果安装了vsftpd会打印相关版本信息,否则没有任何信息
2、yum -y install vsftpd 安装vsftpd
安装过程很简单,是自动安装的,安装完成后有成功的提示。
rpm -e vsftpd 卸载
3、配置防火墙端口
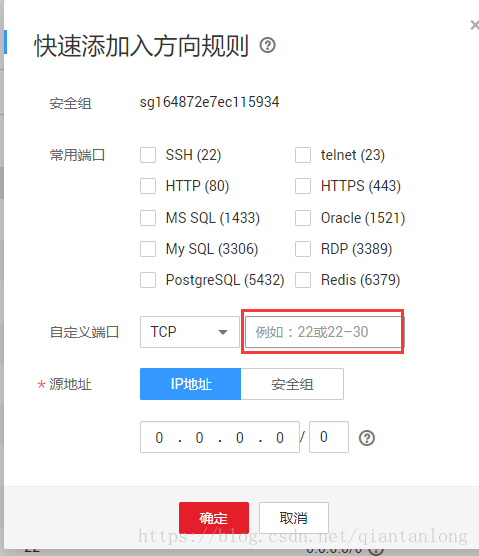
ftp服务需要20、21两个端口,执行下面的开放端口命令
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=20/tcp --permanent 开放20端口
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=21/tcp --permanent 开放21端口
firewall-cmd --reload重新载入防火墙规则
firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports列出开开放的端口
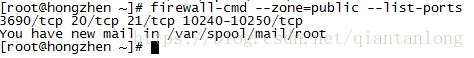
看到20、21端口开放就正面配置好了。
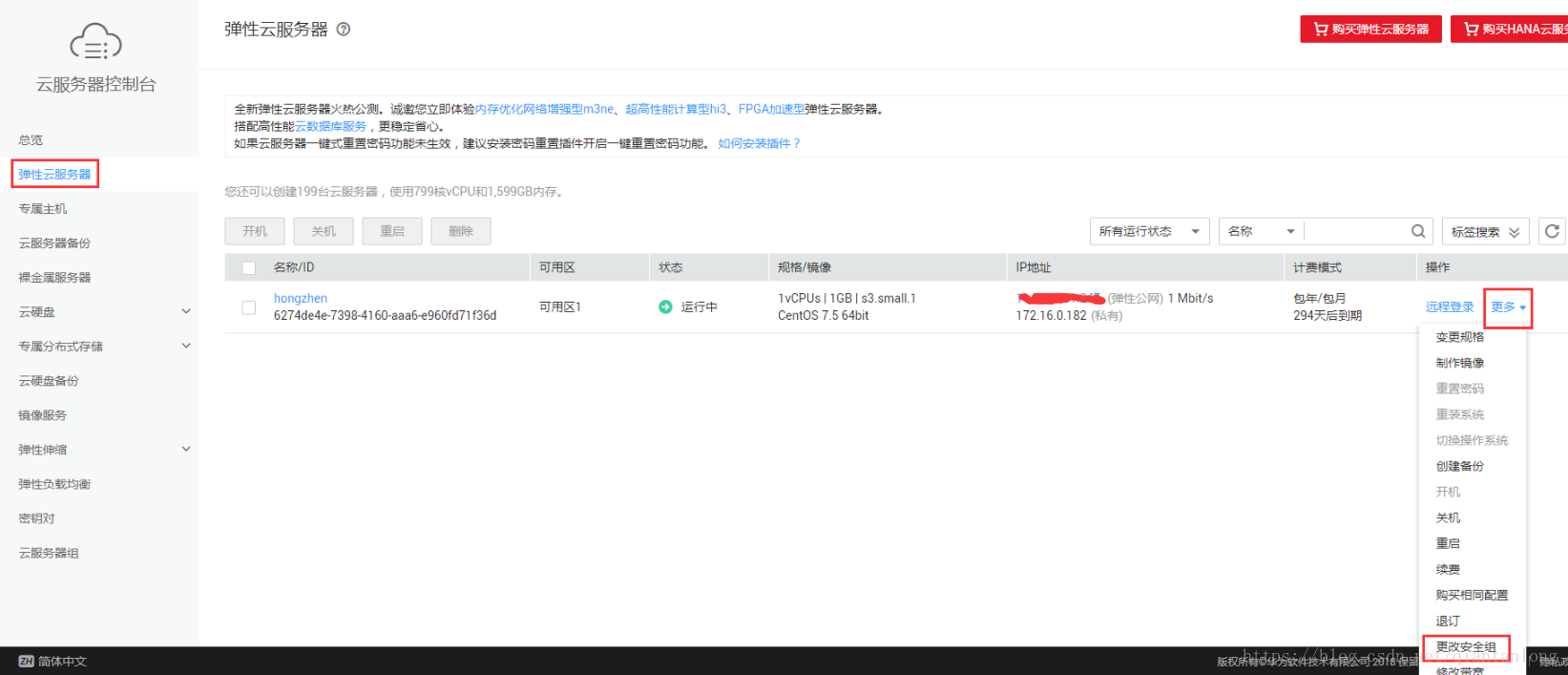
4、配置华为云的安全组策略
控制台-弹性云服务器(ECS)-更多-更改安全组
管理安全组:
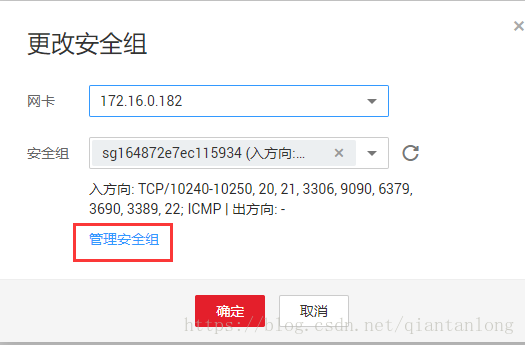
配置规则:
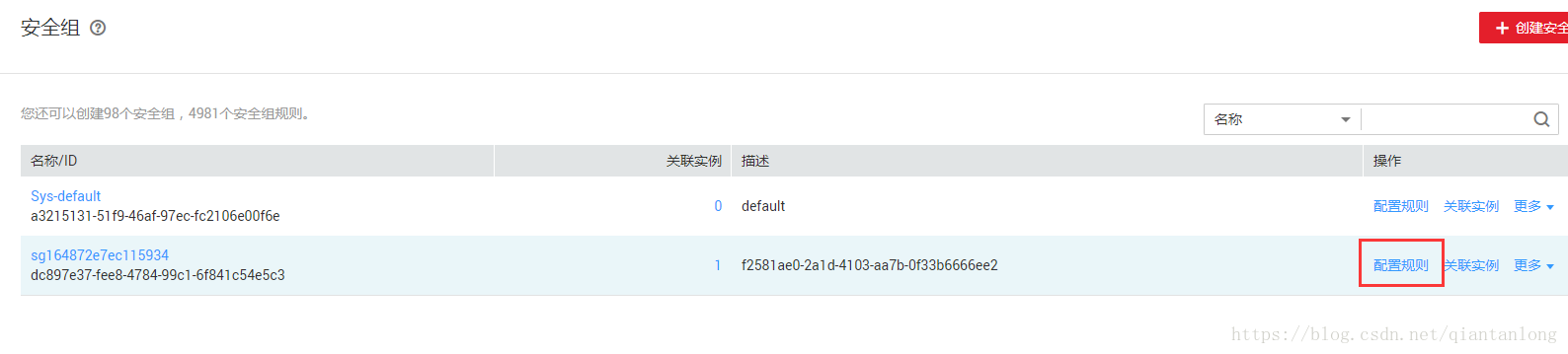
添加规则:
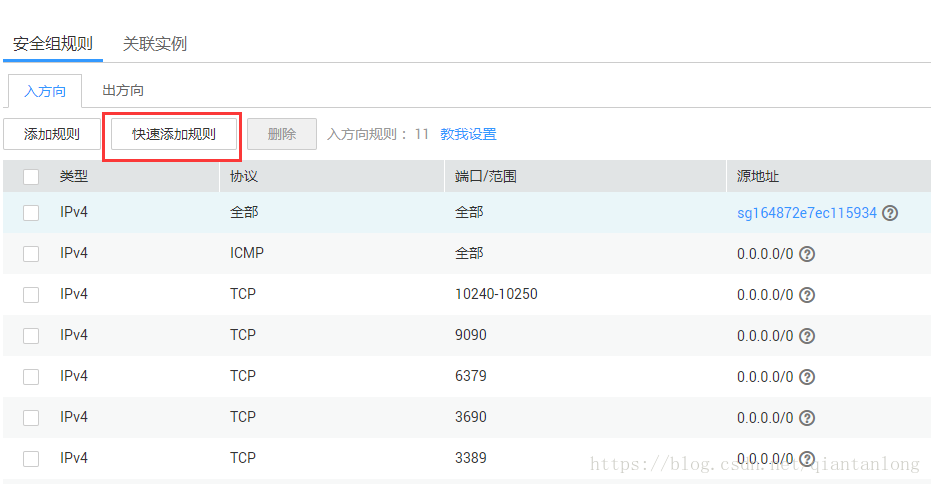
添加需要的20、21端口号:
二、配置vsftpd
1、启动vsftpd
systemctl start vsftpd 启动服务
systemctl restart vsftpd 重启服务
systemctl stop vsftpd 停止服务
netstat -ntpl|grep 21 查看21端口占用情况

2、配置vsftpd.conf文件
/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
# Example config file /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
#
# The default compiled in settings are fairly paranoid. This sample file
# loosens things up a bit, to make the ftp daemon more usable.
# Please see vsftpd.conf.5 for all compiled in defaults.
#
# READ THIS: This example file is NOT an exhaustive list of vsftpd options.
# Please read the vsftpd.conf.5 manual page to get a full idea of vsftpd's
# capabilities.
#
# Allow anonymous FTP? (Beware - allowed by default if you comment this out).
anonymous_enable=NO取消匿名登录
#
# Uncomment this to allow local users to log in.
# When SELinux is enforcing check for SE bool ftp_home_dir
local_enable=YES
#
# Uncomment this to enable any form of FTP write command.
write_enable=YES
#
# Default umask for local users is 077. You may wish to change this to 022,
# if your users expect that (022 is used by most other ftpd's)
local_umask=022
#
# Uncomment this to allow the anonymous FTP user to upload files. This only
# has an effect if the above global write enable is activated. Also, you will
# obviously need to create a directory writable by the FTP user.
# When SELinux is enforcing check for SE bool allow_ftpd_anon_write, allow_ftpd_full_access
#anon_upload_enable=YES
#
# Uncomment this if you want the anonymous FTP user to be able to create
# new directories.
#anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES
#
# Activate directory messages - messages given to remote users when they
# go into a certain directory.
dirmessage_enable=YES
#
# Activate logging of uploads/downloads.
xferlog_enable=YES
#
# Make sure PORT transfer connections originate from port 20 (ftp-data).
connect_from_port_20=YES
#
# If you want, you can arrange for uploaded anonymous files to be owned by
# a different user. Note! Using "root" for uploaded files is not
# recommended!
#chown_uploads=YES
#chown_username=whoever
#
# You may override where the log file goes if you like. The default is shown
# below.
#xferlog_file=/var/log/xferlog
#
# If you want, you can have your log file in standard ftpd xferlog format.
# Note that the default log file location is /var/log/xferlog in this case.
xferlog_std_format=YES
#
# You may change the default value for timing out an idle session.
#idle_session_timeout=600
#
# You may change the default value for timing out a data connection.
#data_connection_timeout=120
#
# It is recommended that you define on your system a unique user which the
# ftp server can use as a totally isolated and unprivileged user.
#nopriv_user=ftpsecure
#
# Enable this and the server will recognise asynchronous ABOR requests. Not
# recommended for security (the code is non-trivial). Not enabling it,
# however, may confuse older FTP clients.
#async_abor_enable=YES
#
# By default the server will pretend to allow ASCII mode but in fact ignore
# the request. Turn on the below options to have the server actually do ASCII
# mangling on files when in ASCII mode.
# Beware that on some FTP servers, ASCII support allows a denial of service
# attack (DoS) via the command "SIZE /big/file" in ASCII mode. vsftpd
# predicted this attack and has always been safe, reporting the size of the
# raw file.
# ASCII mangling is a horrible feature of the protocol.
#ascii_upload_enable=YES
#ascii_download_enable=YES
#
# You may fully customise the login banner string:
#ftpd_banner=Welcome to blah FTP service.
#
# You may specify a file of disallowed anonymous e-mail addresses. Apparently
# useful for combatting certain DoS attacks.
#deny_email_enable=YES
# (default follows)
#banned_email_file=/etc/vsftpd/banned_emails
#
# You may specify an explicit list of local users to chroot() to their home
# directory. If chroot_local_user is YES, then this list becomes a list of
# users to NOT chroot().
# (Warning! chroot'ing can be very dangerous. If using chroot, make sure that
# the user does not have write access to the top level directory within the
# chroot)
chroot_local_user=YES允许系统用户登录ftp
#chroot_list_enable=YES
# (default follows)
#chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list
#
# You may activate the "-R" option to the builtin ls. This is disabled by
# default to avoid remote users being able to cause excessive I/O on large
# sites. However, some broken FTP clients such as "ncftp" and "mirror" assume
# the presence of the "-R" option, so there is a strong case for enabling it.
#ls_recurse_enable=YES
#
# When "listen" directive is enabled, vsftpd runs in standalone mode and
# listens on IPv4 sockets. This directive cannot be used in conjunction
# with the listen_ipv6 directive.
listen=YES监听ipv4连接
#
# This directive enables listening on IPv6 sockets. By default, listening
# on the IPv6 "any" address (::) will accept connections from both IPv6
# and IPv4 clients. It is not necessary to listen on *both* IPv4 and IPv6
# sockets. If you want that (perhaps because you want to listen on specific
# addresses) then you must run two copies of vsftpd with two configuration
# files.
# Make sure, that one of the listen options is commented !!
#listen_ipv6=YES监听ipv6连接,这个与ipv4连接冲突,二选一
pam_service_name=vsftpd
#userlist_enable=YES
tcp_wrappers=YES
allow_writeable_chroot=YES限制用户只能操作/home/用户名这个目录
以下是跟被动模式相关配置:
pasv_enable=yes 被动模式启动
pasv_max_port=10250 启动的最大端口
pasv_min_port=10240 启动的最小端口
端口设置需要防火墙开启、华为云需要配置安全组
pasv_address=114.1*6.*1.*7 华为云主机的IP,改为你自己的运服务器IP
pasv_addr_resolve=yes 配合pasv_address开启允许欺骗
3、重启vsftpd
systemctl restart vsftpd 重启服务
4、新建用户test
adduser test 新建用户,这个是Linux系统的用户,可以登录ftp用户。
passwd test 设置用户密码
用户密码过于简单时,会提示无效密码,不必理会,密码是可以正常生效的。
5、在浏览器或ftp客户端软件(filezilla等)登录ftp
此时就可以在浏览器、资源管理器、或ftp客户端软件上登录ftp了,输入用户名、密码。
三、常见问题的解决
1、无法建立连接

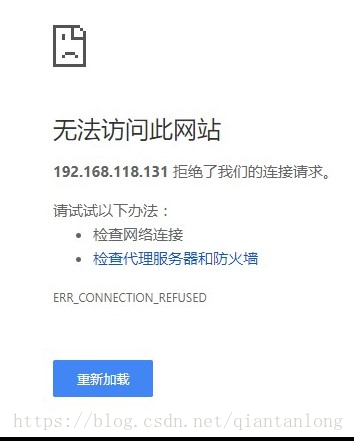
解决方法:
可能的原因:
a、检查是否启动vsftpd服务
systemctl status vsftpd.service检查vsftpd的状态
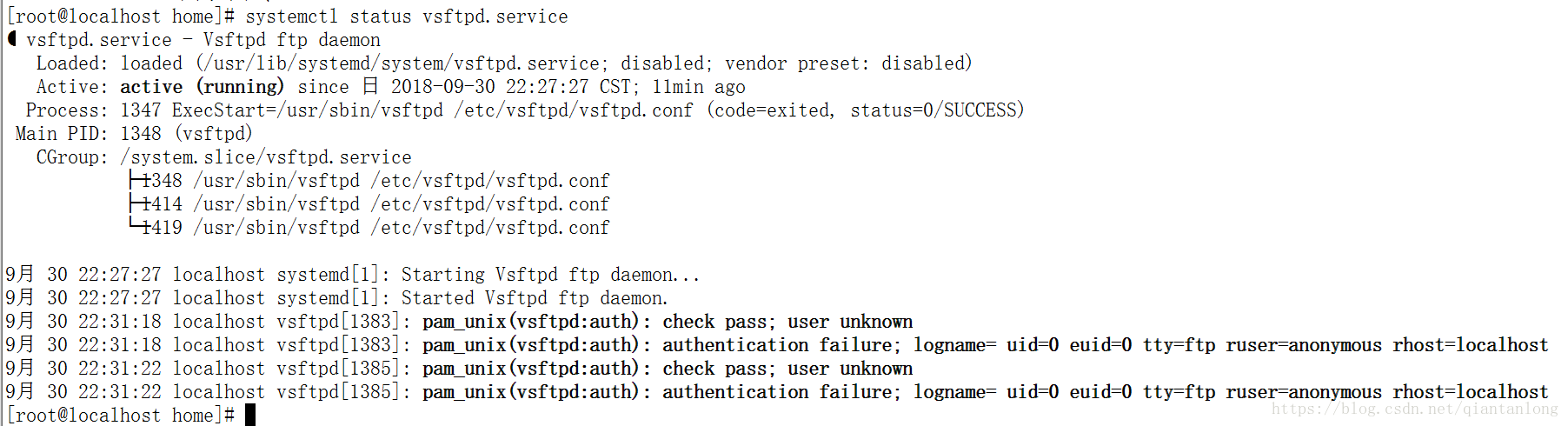
netstat -ntpl|grep 21 查看21端口占用情况

b、检查防火墙的配置,是否开启20、21端口
详细配置,参考上面的防火墙配置
c、关闭Selinux(临时关闭,重启后失效。如果想永久关闭,自行百度进行设置)
getenforce 查看Selinux的状态
[root@localhost ~]# getenforce
Enforcing开启状态
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# getenforce
Permissive关闭状态
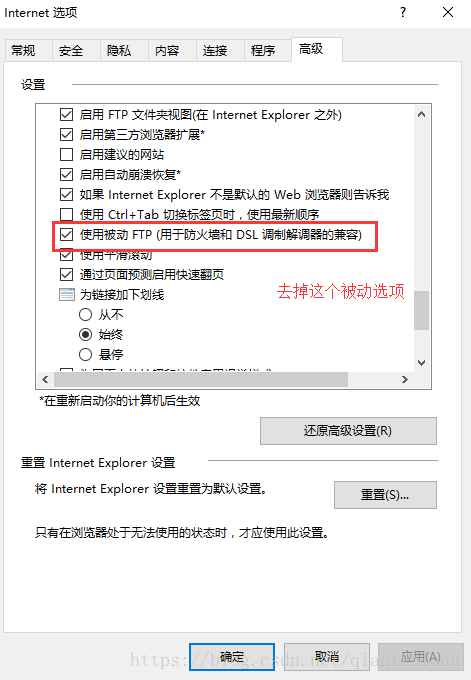
2、命令行可以登录,但是浏览器和资源管理器无法登录
这里涉及到vsftpd的主动模式和被动模式的问题,默认情况下,vsftpd服务不支持被动模式,需要进行设置。
a、在vsftpd.conf配置文件中设置被动模式的支持,支持浏览器和资源管理器访问
以下是跟被动模式相关配置:
pasv_enable=yes 被动模式启动
pasv_max_port=10250 启动的最大端口
pasv_min_port=10240 启动的最小端口
端口设置需要防火墙开启、华为云需要配置安全组
pasv_address=114.116.91.247 华为云主机的IP
pasv_addr_resolve=yes 配合pasv_address开启允许欺骗
b、在IE浏览器的选项中进行配置,临时解决IE浏览器和资源管理器无法访问的问题,但是其他浏览器不一定能够访问,这种方式不推荐
c、filezilla无法访问,原因同浏览器无法访问一样
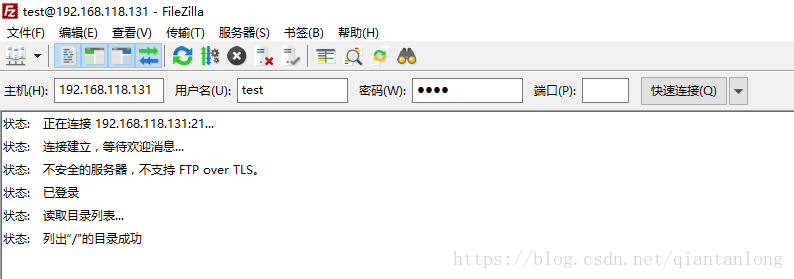
解决方法:
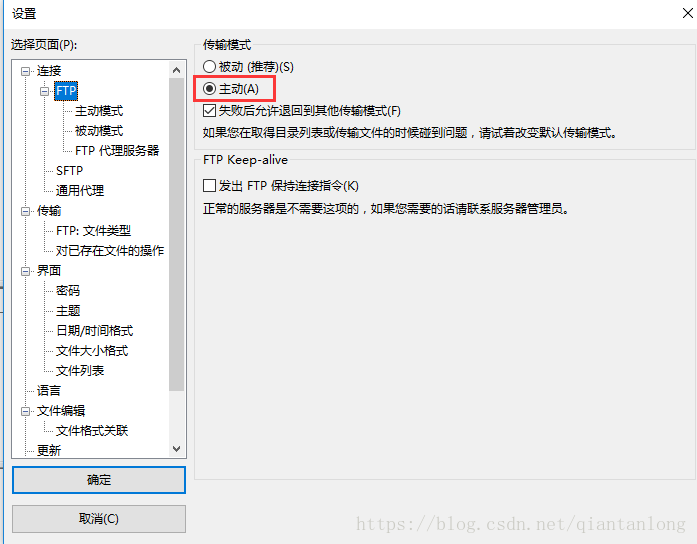
filezilla的软件版本和语言不同,界面可能不同,但是原理是一样的。vsftpd没有进行被动模式的配置,不支持被动模式访问。只有设置成主动模式访问就可以正常访问了。